How to Update appsettings.json Files
The Intent.VisualStudio.Projects module automatically generates the appsettings.json file for supported .NET project types.
How to Update from a Template
To apply additional configuration to an appsettings.json file, use the ApplyAppSetting extension method within your Template. For example:
public override void BeforeTemplateExecution()
{
this.ApplyAppSetting(
field: "CustomSectionName:SomeStringField",
value: "Some Value");
this.ApplyAppSetting(
field: "OtherCustomSectionName",
value: new
{
IntValue = 10,
StrValue = "My String"
});
}
Note
This extension method requires Intent.Modules.Common.CSharp NuGet package to be installed in your module project.
Important
This can only be invoked after construction of the template, otherwise the template which responds to this event might not yet have been constructed.
Placing this method in the override of either the AfterTemplateRegistration or BeforeTemplateExecution methods will ensure it is called only after all other templates have been constructed.
In the example above, the appsettings.json file will include the following:
{
// ... other configuration...
"CustomSectionName": {
"SomeStringField": "Some Value"
},
"OtherCustomSectionName": {
"IntValue": 10,
"StrValue": "My String"
}
}
How to update from a Factory Extension
It is also possible to apply additional configuration to an appsettings.json file using a Factory Extension with the EventDispatcher. For example:
protected override void OnAfterTemplateRegistrations(IApplication application)
{
base.OnAfterTemplateRegistrations(application);
application.EventDispatcher.Publish(new AppSettingRegistrationRequest(
key: "CustomSectionName:SomeStringField",
value: "Some Value"));
application.EventDispatcher.Publish(new AppSettingRegistrationRequest(
key: "OtherCustomSectionName",
value: new
{
IntValue = 10,
StrValue = "My String"
}));
}
Note
When providing a complex value, you should pass in an anonymous C# object as demonstrated above. Passing a JSON formatted string is not supported and will result in the string being escaped and written as a single value in the appsettings.json file, rather than being parsed as a JSON object.
The resulting appsettings.json file will be the same as in the previous Template example:
{
// ... other configuration...
"CustomSectionName": {
"SomeStringField": "Some Value"
},
"OtherCustomSectionName": {
"IntValue": 10,
"StrValue": "My String"
}
}
Variable field names
To create appsettings.json entries with variable field names, or to update an existing section, you can use the following syntax:
this.ApplyAppSetting(
field: "OtherCustomSectionName:AdditionalStringValue",
value: "AdditionalStrValue");
Executing this method after the previous above example, your appsettings.json file will look like the following:
{
// ... other configuration...
"CustomSectionName": {
"SomeStringField": "Some Value"
},
"OtherCustomSectionName": {
"IntValue": 10,
"StrValue": "My String",
"AdditionalStringValue" : "AdditionalStrValue"
}
}
Environment specific appsettings.json files
To enable Intent Architect to generate separate appsettings.json files for each environment, you must configure the runtime environments in the Visual Studio Designer.
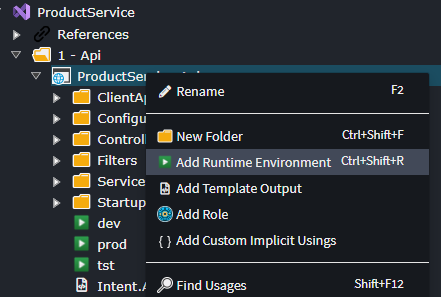
This configuration will generate three additional appsettings files, in addition to the base appsettings.json file.
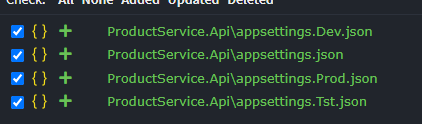
When the ApplySetting method is called, the runtime environment can be supplied, which will result in the setting only being applied to the relevant appsettings file.
this.ApplyAppSetting(
field: "ProductionOnlySetting",
value: "ProductionValue",
runtimeEnvironment: "prod");