Intent.Modelers.Services.DomainInteractions
This module provides designer support for our CRUD Modules.
Domain Interaction Settings
This section defines how the application interacts with the Domain Layer. Each setting influences how data is mapped, queried, and updated within the domain.
Default Mapping Mode
The Intent Architect mapping mode to use. Defaults to Advanced Mapping. Generally should not be changed.
Default Query Implementation
Determines how entities are retrieved from the Domain Layer and mapped to DTOs.
- Default: Uses
AutoMapper's traditional mapping method, leveraging Intent Architect mapping configurations to map Domain Entities to DTOs. - Project To: Uses
AutoMapper ProjectTo, enabling optimized database queries by mapping directly within LINQ expressions based on Intent Architect configurations.
Null Child Update Implementation
Controls how null child entities in a request are handled when updating the Domain Layer.
Ignore
If aNULLchild entity is present in a service request, the existing child entity in the domain remains unchanged.// if a NULL ProductDetails is received, existing ProductDetails details will remain unchanged if (request.ProductDetails != null) { entity.ProductDetails ??= new Domain.Entities.ProductDetails(); entity.ProductDetails.Name = request.ProductDetails?.Name; entity.ProductDetails.Qty = request.ProductDetails?.Qty; }Set to NULL (Default behavior)
If aNULLchild entity is present in a service request, the corresponding child entity in the domain is explicitly set toNULL.// if a NULL ProductDetails is received, existing ProductDetails details will be set to null if (request.ProductDetails != null) { entity.ProductDetails ??= new Domain.Entities.ProductDetails(); entity.ProductDetails.Name = request.ProductDetails?.Name; entity.ProductDetails.Qty = request.ProductDetails?.Qty; } else { entity.ProductDetails = null; }
Pagination
When modeling your services any Query and/or service Operation which return PagedResult<T> will be realized as a paginated implementation.
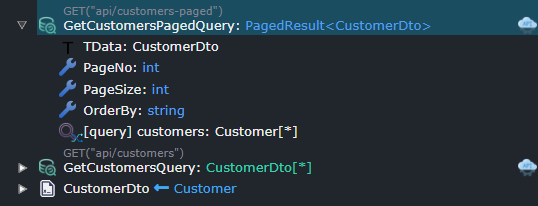
A paginated end point would typically have the following parameters:
PageNo(int), the page you wish to return data from. (This sequence is 1 based i.e. 1,2,3...)PageSize(int), the no of items to return per page.OrderBy(string), string based order by clause.
If you would like 0 based page Indexing (0,1,2,...) replace PageNo with PageIndex.
If you want don't want to specify and order by clause, you can remove this parameter from your Query or service Operation.
string based order by clause examples
Given a Customer with a Name and Surname these would all be valid order by clauses.
- "Name" - order by Name ascending
- "Surname" - order by Surname ascending
- "Name asc" - order by Surname ascending
- "Surname desc" - order by Surname descending
- "Surname desc, Name asc" - order by Surname descending, then Name ascending
You can use the Paginate context menu option on Query and/or service Operation elements to easily configure these endpoints.
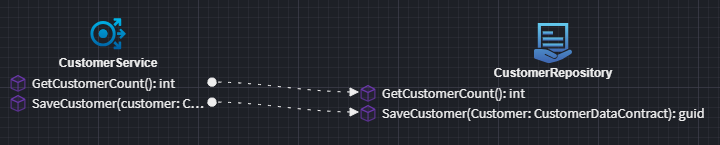
Modeling a Repository Operation Call
To model the invocation of a Repository Operation, two accelerators are available, supporting either CQRS or Traditional service styles.
Alternatively, you can create the services, invocations, and mappings manually without using the provided accelerators, offering full control over the structure and implementation.
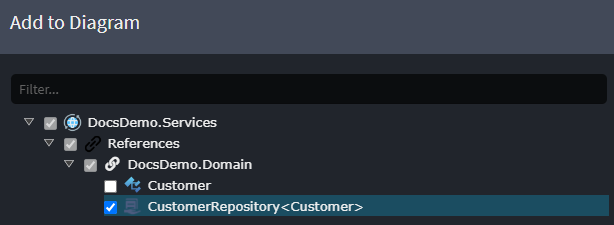
Reference the Repository
- In the Service Designer, within a diagram, right-click and select
Add to Diagram. - Choose the previously created
Repositoryand click Done.
Create the Service
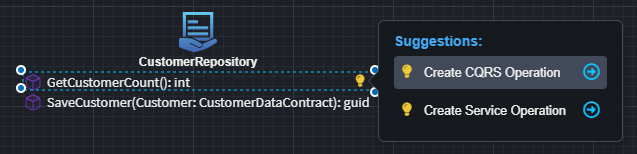
Once the repository is added to the diagram, a suggestion will appear to either:
- Create a CQRS Operation
- Create a Service Operation
These options allow you to quickly scaffold a service that invokes the repository operation.
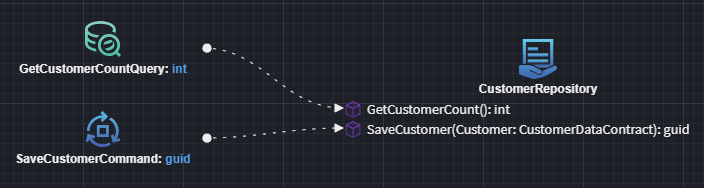
CQRS Operation
Use the Create CQRS Operation option to generate either a Command or a Query that calls the repository:
Traditional Service Operation
Use the Create Service Operation option to generate a traditional service method for calling the repository: