Intent.ApiGateway.Ocelot
This module implements the Ocelot API Gateway in a ASP.NET Core application.
What is Ocelot?
Ocelot is aimed at people using .NET running a microservices / service-oriented architecture that need a unified point of entry into their system. -Website
Modeling API Gateway Routes
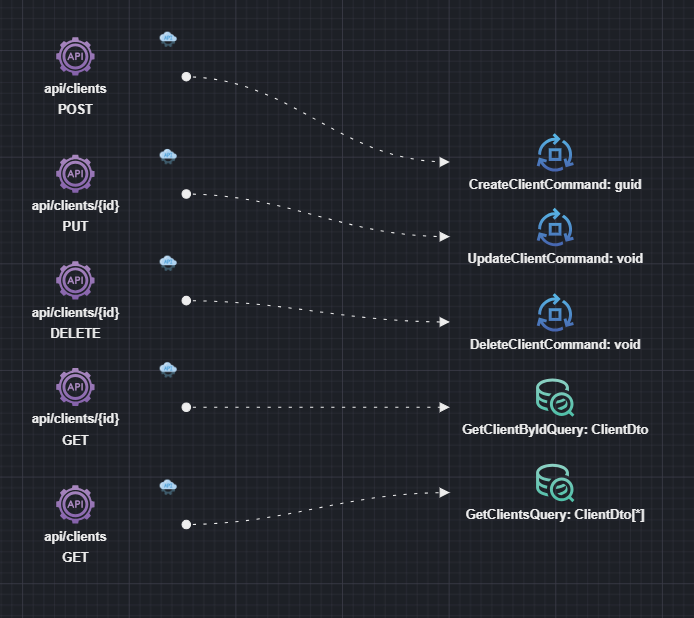
The following steps are performed inside the Services designer:
- First you need to add a reference to a Services package containing all the downstream service endpoints.
- Right-click on the Service package and select
Add Package Reference. - Locate the Service package from another Intent Architect application that will act as the downstream service.
- Click on DONE.
- Right-click on the Service package and select
- Add downstream endpoints:
- Right-click on the diagram background and select
Add to diagram. - Select the downstream endpoints you would like to connect to. They would be in the form of
Command/Query/Serviceendpoints. - Click on DONE.
- Right-click on the diagram background and select
- Add Api Gateway routes:
- Right-click on the diagram background and add a new
Api Gateway Routeelement. - Right-click on it and select
New Route Association. - Select a downstream endpoint to connect to and click to snap it into place.
- Right-click on the diagram background and add a new
Inspect the ocelot.json file
The routes will be generated inside the ocelot.json file:
{
"Routes": [
{
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/api/clients",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [
"Post"
],
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/api/clients",
"DownstreamHttpMethod": "POST",
"DownstreamHostAndPorts": [
{
"Host": "{Clients.Host.Name}"
}
]
},
// ...
You will see that each route entry has a Host value corresponding to the package name being imported. This is a substitution of the actual host name and port number.
Configure those services inside the appsettings.json file:
{
//...
"Ocelot": {
"Hosts": {
"Clients.Host.Name": "https://localhost:44300"
}
}
}