Intent.AspNetCore.Docker
The module installs Docker support into your ASP.Net Core solution, similar to how Visual Studio would do if you select enable Docker support on solution creation.
Running and debugging your solution under Docker
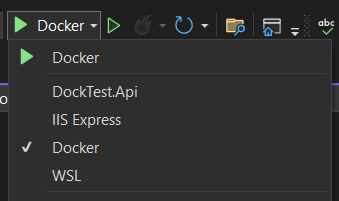
The easiest way to run or debug your solution in Visual Studio is to simply choose "Docker" as your Debug Target:
Configuration and Environment Variables
To configure your .NET app, typically an ASP.NET Core app, you can use appsettings.json and/or environment variables.
appsettings.json: This file is used to store configuration settings. ASP.NET Core supports multiple
appsettings.jsonfiles for different environments, such asappsettings.Development.jsonandappsettings.Production.json. These files allow you to override settings based on the environment your application is running in. For more details, see ASP.NET Core Configuration.Environment Variables: ASP.NET Core can also read configuration settings from environment variables. These can be set in the
launchSettings.jsonfile or directly in the Dockerfile or Docker Compose file. Environment variables prefixed withASPNETCORE_orDOTNET_are to override specific launch or system variables. For more information on environment variables and their precedence, refer to ASP.NET Core Environment Variables.
Environment variables have a higher preference than appsettings.json settings. This means that if a setting is defined in both appsettings.json and as an environment variable,
the environment variable's value will be used. This behavior is particularly useful for sensitive information that should not be stored in source control or for settings that vary
between environments.
For example, consider the following appsettings.json configuration:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=aspnet-WebApplication1-53bc9b9d-9d6a-45d4-8429-2a2761773502;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
}
And an environment variable:
In this case, the environment variable ConnectionStrings__DefaultConnection will override the DefaultConnection setting in appsettings.json.
Basic Docker cli commands
Docker build
From a terminal in the folder of the project with the entry point of your application:
docker build -f ./Dockerfile -t <image-name> ..
-f specifies the Dockerfile to use, -t specifies the docker image name, and the .. at the end specifies the working directory.
See Docker's documentation for more information.
Docker run
docker run -P <image-name> ..
-P publishes exposed ports to random ports.
See Docker's documentation for more information.
Pass Environments variables via arguments
Execute docker command:
docker run -it --name "your-container-name" -e ConnectionStrings__DefaultConnection="Server=myserver;Database=mydatabase;User Id=myuser;Password=mypassword;" <image-name>
Pass ENV file with configured Environment Variables
Create an .env file:
ConnectionStrings__DefaultConnection=Server=myserver;Database=mydatabase;User Id=myuser;Password=mypassword;
Execute docker command:
docker run -it --name "your-container-name" --env-file ./.env <image-name>
Troubleshooting
There are scenarios where you need to clear out your local .vs folder.
- If you change your development hosting option i.e., from Docker to Local Kestrel.
- To regenerate the Docker certificate setup, when running the dockerized solution.