Intent.Entities.BasicAuditing
Basic auditing in database management is a pattern used to track key information about the creation and last modification of records. This involves adding fields to your SQL table such as CreatedBy, CreatedDate, UpdatedBy and UpdatedDate. This pattern offers a straightforward way to capture and display who initially created a record and who last modified it, along with the relevant timestamps. However, it is important to note that this approach provides a snapshot of the most recent actions rather than a comprehensive audit trail of all changes made over time.
Note
This is not an Audit Trail but merely a way to determine who touched an Entity and when.
General usage pattern
Select an Entity in the Domain Designer.
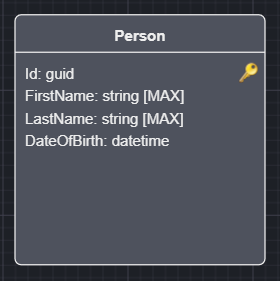
Right click and select Toggle Basic Auditing.
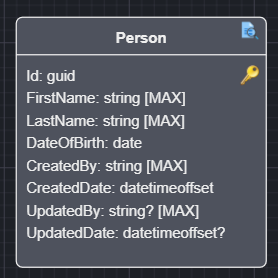
Your Entity will now be extended with the following attributes:
- CreatedBy - User Identity that created this Entity instance.
- CreatedDate - Timestamp when creation took place.
- UpdatedBy - User Identity that updated this Entity instance.
- UpdatedDate - Timestamp when creation took place.
Note
It is worth noting that the "updated" attributes remain null upon creation and only get populated when an update has taken place.
Application Settings which affect this module
This module uses the ICurrentUserService to determine the current user's identity.
public interface ICurrentUserService
{
<UserID Type>? UserId { get; }
string? UserName { get; }
...
}
Basic Auditing Settings - User Identity to Audit
This setting allows you to select which field you would like to use as your audit of the user's identity, the options are:
- User Id (default), will use the
UserIdproperty and is typically more technical in nature. - User Name, will use the
UserNameproperty.
Identity Settings - UserId Type
This setting allows you to specify what the type of the UserId on the ICurrentUserService should be. Allowing you to customize how you want you audi data persisted.
- string (default)
- guid
- int
- long
The Audit fields of CreatedBy and UpdatedBy will respect the above settings.
Note
If you adjust the above settings after you have already modeled Classes with basic auditing, you can Right Click on any Audited class and select the Synchronize Auditing Identifiers option. This will update your existing Domain Model such that the CreatedBy and UpdatedBy attributes have the newly configured types.
This introduces a IAuditible interface in your Domainproject which gets added to class Entities that are decorated with the Basic Auditing stereotype.
public interface IAuditable
{
string CreatedBy { get; set; }
DateTimeOffset CreatedDate { get; set; }
string? UpdatedBy { get; set; }
DateTimeOffset? UpdatedDate { get; set; }
}
Example:
public class Person : IHasDomainEvent, IAuditable
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
public string CreatedBy { get; set; }
public DateTimeOffset CreatedDate { get; set; }
public string? UpdatedBy { get; set; }
public DateTimeOffset? UpdatedDate { get; set; }
public List<DomainEvent> DomainEvents { get; set; } = new List<DomainEvent>();
}
Intent.EntityFrameworkCore integration
If you have the Intent.EntityFrameworkCore module installed, your DbContext will also be extended to automatically populate the Entities with the IAuditable interface using the injected ICurrentUserService to resolve the "current user" at the time.
public override async Task<int> SaveChangesAsync(
bool acceptAllChangesOnSuccess,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
SetAuditableFields();
// ...
}
Intent.CosmosDB integration
If you have Intent.CosmosDB module installed, the CosmosDBRepositoryBase will be updated to set the auditable fields as appropriate.