Intent.Eventing.AzureServiceBus
This module provides patterns for working with Azure Service Bus directly.
What is Azure Service Bus?
Azure Service Bus is a fully managed enterprise message broker with message queues and publish-subscribe topics. It enables reliable message delivery, message routing, and data transfers between different applications and services. Service Bus helps you decouple applications and services from each other, providing features like message sessions, transactions, ordering, and duplicate detection.
For more information on Azure Service Bus, check out their official docs.
Modeling Integration Events and Commands
Modeling Integration Events can be achieved from within the Services designer.
This module automatically installs the Intent.Modelers.Eventing module which provides designer modeling capabilities for integration events and commands.
For details on modeling integration events and commands, refer to its README.
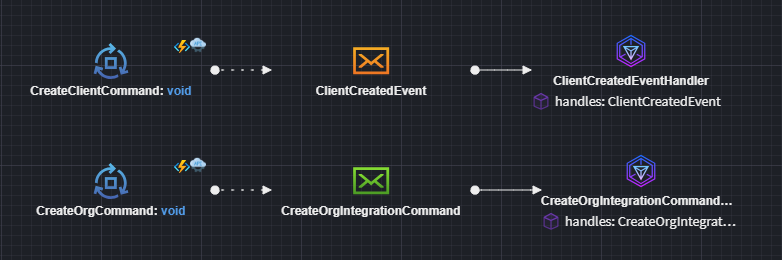
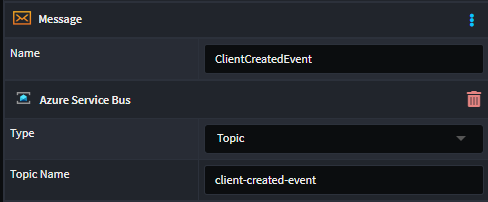
You can model Integration Events (orange Message envelope element), and it will automatically configure to work against a Topic with a derived name.
However, you can customize the name of the Topic by applying an Azure Service Bus stereotype and setting the Type to Topic (or Queue) and Topic Name to the desired name.
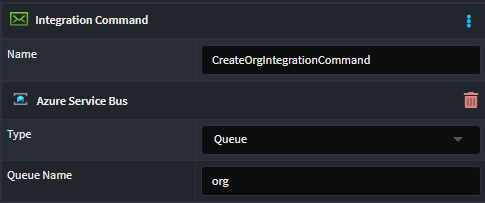
Similarly, can model Integration Commands (green Message envelope element), and it will automatically configure to work against a Queue with a derived name.
However, you can customize the name of the Topic by applying an Azure Service Bus stereotype and setting the Type to Queue (or Topic) and Queue Name to the desired name.
Azure Service Bus Implementation
Provides an Azure Service Bus specific implementation of the IEventBus interface for dispatching messages.
Message Publishing
Message publishing can be done through the IEventBus interface using the Publish method for Topics and Send for Queues.
Message Consumption
For every message subscribed to in the Services Designer will receive its own Integration Event handler.
The is what the Business logic Integration Event handler looks like:
[IntentManaged(Mode.Merge, Signature = Mode.Fully)]
public class ClientCreatedIntegrationEventHandler : IIntegrationEventHandler<ClientCreatedEvent>
{
[IntentManaged(Mode.Ignore)]
public ClientCreatedIntegrationEventHandler()
{
}
[IntentManaged(Mode.Fully, Body = Mode.Ignore)]
public async Task HandleAsync(ClientCreatedEvent message, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
// Business logic here
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
Note
This module will not be generating consumer code automatically for you. Look at the Related Modules section to see which modules cause this to happen.
Working with Multiple Message Bus Providers
This module can coexist with other message bus implementations in the same application. When multiple providers are installed, Intent Architect automatically generates a Composite Message Bus that intelligently routes messages based on configuration.
Designating Messages for Azure Service Bus
When you have only this provider installed, all messages automatically use it—no configuration needed.
When you have multiple providers installed, you must designate which messages should be handled by Azure Service Bus using the Message Bus stereotype:
- Right-click on a Package or Folder in the Services designer
- Select Add Stereotype → Message Bus
- In the stereotype properties, select
Azure Service Busfrom the Providers list
The stereotype can be applied at multiple levels:
- Package level: All messages in the package use the selected provider(s)
- Folder level: All messages in the folder inherit the designation
- Message level: Individual message-level control (rarely needed)
Stereotype Inheritance: Child elements inherit their parent's Message Bus stereotype automatically, so you typically only need to set it at the package or folder level. Intent handles all the routing transparently.
Generated Code Filtering
When multiple providers are installed:
- Azure Service Bus only generates handlers, consumers, and configuration for messages marked with its provider designation
- Messages designated for other providers are ignored by this module
- Messages can be marked for multiple providers and will be handled by each
Additional Resources
For comprehensive details on the Composite Message Bus architecture and design, see the Intent.Eventing.Contracts documentation.
Configuring Service Bus
When you're publishing using Azure Service Bus, you will need to configure it in your appsettings.json file.
{
"AzureServiceBus":{
"CreateOrg": "create-org",
"ClientCreated": "client-created",
"ConnectionString": "Endpoint=sb://your-namespace.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=RootManageSharedAccessKey;SharedAccessKey=yourkey"
}
}
Related Modules
Intent.AzureFunctions.AzureServiceBus
This module handles the consumer code for Azure Service Bus when Azure Functions is selected as the hosting technology.
Intent.AspNetCore
This module introduces ASP.NET Core as the hosting platform for your application. When this is detected, a special background service is added to listen for inbound messages from Azure Service Bus.
Intent.WindowsServiceHost
This module introduces minimal hosting components to allow for background processing. When this is detected, a special background service is added to listen for inbound messages from Azure Service Bus.
Note
Not seeing the hosting technology you're looking for? Please reach out to us on GitHub or email us at support@intentarchitect.com, and we'll be happy to help.