About Stereotype Definitions
Stereotypes can only be created and applied in Intent Architect Designers if their Stereotype Definitions are accessible. These Definitions need to be created first and can often be found when a Module is installed in your Application. They offer a blueprint that Intent Architect can recognize when trying to apply them.
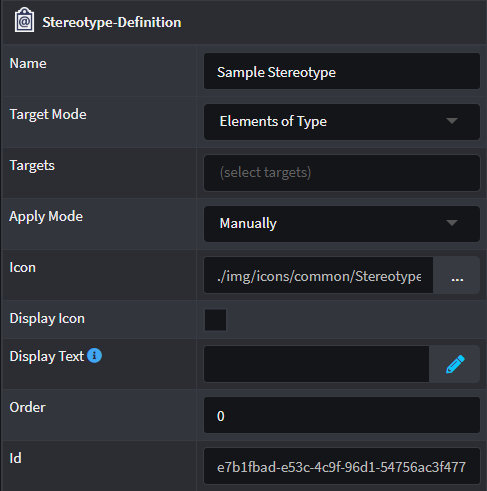
| Property | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Target Mode | Elements of Type | Only allows the Stereotype to be applied on Elements found in the Target property. |
| Elements that reference | Only allows the Stereotype to be applied on Elements' attributes/fields or associations that reference the Elements found in the Target property. |
|
| All elements | No constraints on where the Stereotype can be applied. | |
| Target | Elements found in Designer | The Element types upon which the Stereotype Definition may be applied. |
| Apply mode | Manually | The user has to explicitly apply a Stereotype on a Target Element. |
| On element created | When a Target Element is created, the Stereotype is automatically applied but it can be removed. |
|
| Always | The Stereotype exists permanently on any Target Element and cannot be removed (as long as the Stereotype Definition exists). |
|
| Icon | Formatted Text | Change the icon for the Stereotype by pressing the button with an ellipses. |
| Display Icon | Check box | When selected, the Stereotype's icon will appear in the tree node and visual modellers for elements on which it is applied. |
| Display Text | Function | Using the Javascript language, write a formatted text string that will be used by the Designer to add a Display Text where available. Example: return `[${properties["Router Link"].value}]`. |
| Order | Number | Each Stereotype can be ordered according to this numerical value (in ascending order) in the Properties panel located on the right hand side in Intent Architect within a designer. |
Stereotype Properties
Stereotypes Definitions allow any number of Properties to be added to them. Property names must be unique per Stereotype Definition. By default Stereotype Definition Properties have their Control Type set to Text Box which allows capturing of free text, but there are many other Control Types which can be selected.
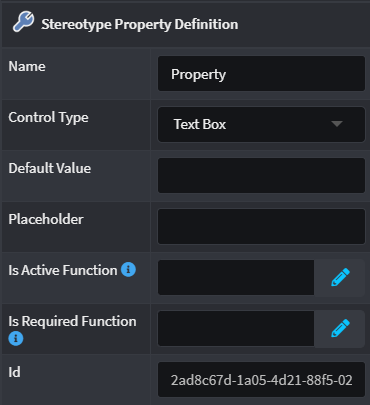
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Text | Specify a friendly name for the Property, spaces and punctuation are allowed. |
| Control Type | Type | Allows the Property to capture a single line of free text that represents a string. See here for more detail. |
| Default Value | Control Type Value | Specify a default value in for this Property depending on the Control Type specified. |
| Placeholder | Text | Specify a description for this Property's input field which a user of the Stereotype can see which describes what is expected. |
| Is Active Function | Javascript | Write a script that returns true/false in order to determine if the Property will be visible/hidden or not. By default this will be Active. |
| Is Required Function | Javascript | Write a script that returns true/false in order to determine if the a value is required for this Property which is validated by Intent Architect. By default this will not be required. |
Control Types
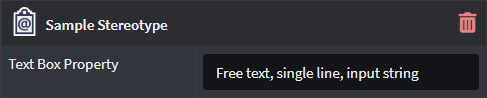
Text Box
Allows the Property to capture a single line of free text that represents a string.
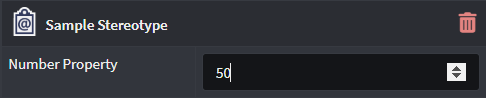
Number
Allows only the capture of a Numerical integer value for this Property.
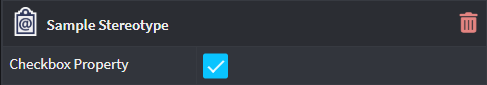
Checkbox
Presents a checkbox to capture a boolean value for the Property.
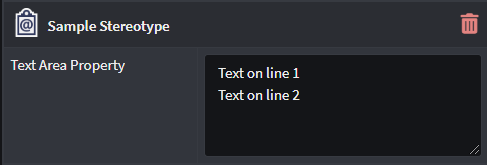
Text Area
Allows the Property to capture multiple-lines of free text that represents a string.
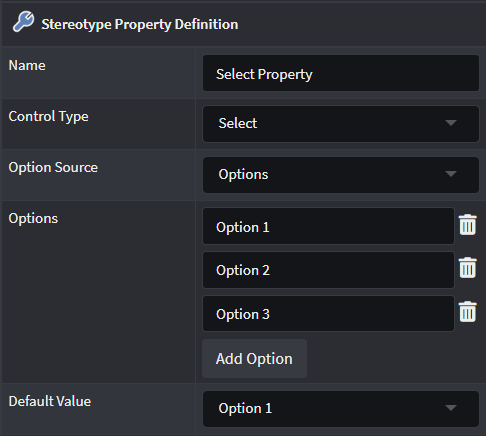
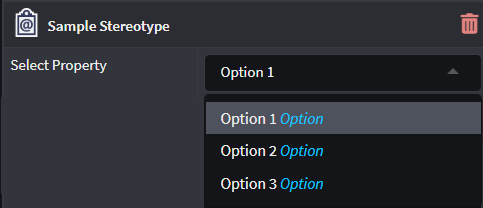
Select/Multi-select
Options
Provides an additional Options field where the Developer can specify explicit options which can be selected for that Stereotype Property.
Lookup element
Provides an additional Lookup types field where the Developer can select Element types in order to make the Property a dropdown control that features instances of those Element types.
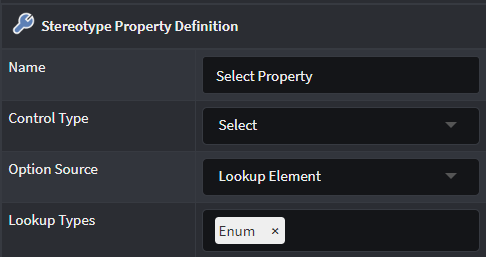
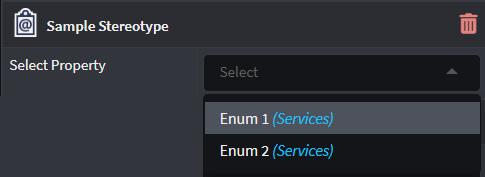
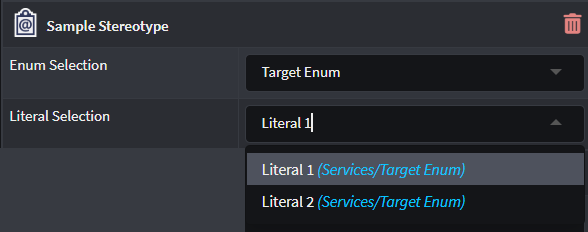
Lookup Children
Provides additional Root Type Function and Lookup types fields where a Developer can determine which Element type's "child elements" can be selected. Use the Lookup types to select the Child-Element to be selected and specify the function to evaluate how to determine the Parent-Element in the Root Type Function field.
Example of selecting Enum Literals from a previously selected Enum:
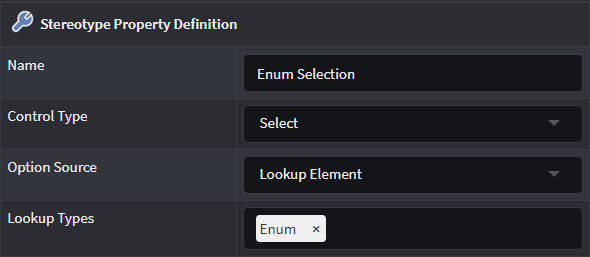
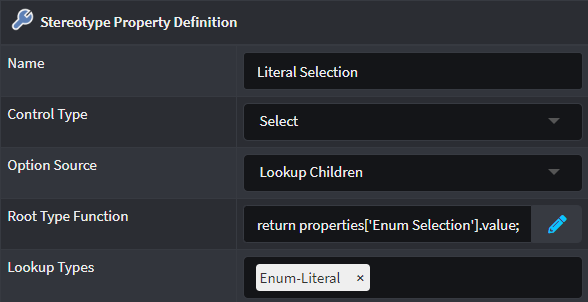
Root Type Function expression:
return properties['Enum Selection'].value;
Javascript Function
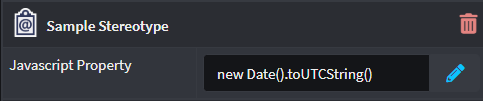
Exposes the Property as a Javascript type field where the Developer can use the built in Javascript editor to define a script which can be leveraged by other Stereotype Properties or Designer elements.
Icon
Exposes the Property as a standard Icon selector which acts in the same manner as the Icon property found on the Stereotype Definition itself.
![]()